Metal additive manufacturing, also called metal 3D printing, produces solid objects in any shape or design from a computer blueprint. It works by stacking thin layers of metal powder and bonding them together. This method allows us to create complex metal objects with precision and flexibility.
Due to its versatility, metal additive manufacturing is successfully employed in industries such as aerospace and healthcare. In this blog, we’re going to discuss the applications of this process across various sectors.
Advantages of Metal Additive Manufacturing
Before we proceed with metal additive manufacturing’s applications in various industries, let’s take a look at a few advantages of this method:
Design Flexibility
Metal AM empowers designers with unprecedented freedom, enabling the fabrication of intricate and custom geometries previously unattainable through conventional methods.
Expedited Prototyping
The technology facilitates rapid iteration and validation of designs, effectively shortening product development cycles and accelerating time-to-market.
Enhanced Material Utilisation
AM minimises material waste by selectively depositing metal powder only where necessary, resulting in cost savings and a more sustainable manufacturing process.
High-Performance Components
It enables the creation of lightweight yet robust parts that are particularly valuable in the aerospace and automotive sectors for optimising fuel efficiency and overall performance.

On-Demand Production
Metal AM enables the production of parts as needed, reducing inventory costs and offering greater flexibility in responding to market demands.
Cost-Efficient Production
By eliminating the need for expensive tooling and moulds, metal AM offers a cost-effective solution for low-volume production and prototyping, streamlining manufacturing processes.
Applications of Metal Additive Manufacturing
Let us discuss some of the most common applications of additive manufacturing techniques and how they have transformed some specific sectors:
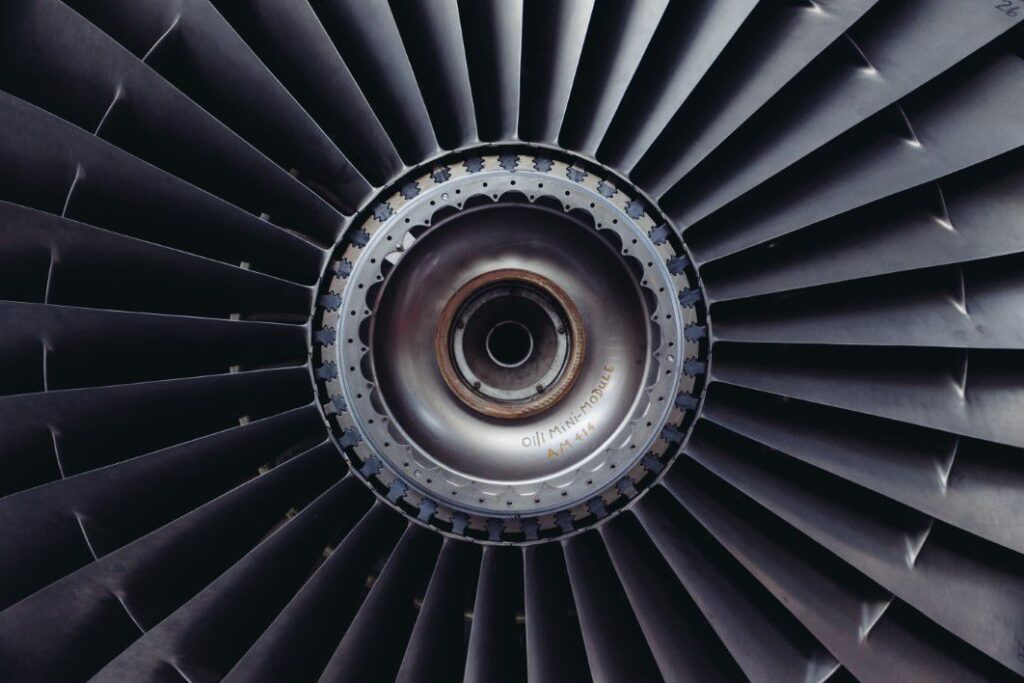
Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace industry, metal additive manufacturing is a game-changer. It can fabricate lightweight, robust components, such as intricate structures and specialised parts.
For instance, turbine blades, fuel nozzles, and brackets demand intricate designs for optimal performance. Metal additive manufacturing (MAF) also allows the creation of complex parts with precision, ensuring they meet stringent aerospace standards.
Additionally, this process’s lightweight yet durable parts are crucial for enhancing fuel efficiency and overall aircraft performance.
Medical Sector
A diverse range of parts is required in medical applications like surgical instruments and anatomical models for preoperative planning. Metal additive manufacturing offers unique advantages in meeting these needs.
For instance, consider the production of patient-specific implants. Traditional methods often require extensive manual shaping of implants to fit individual patients, leading to longer surgical times and increased risk of complications.
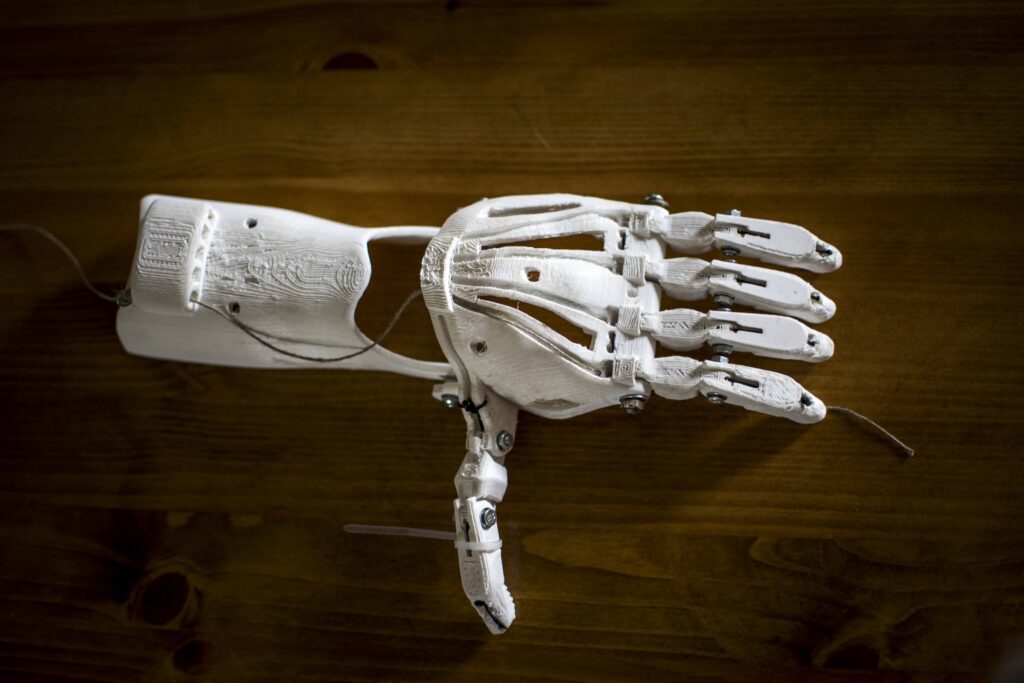

However, with this process, implants can be custom-designed based on patient scans and directly 3D printed with precise geometries tailored to the patient’s anatomy. This improves the fit and functionality of implants, reduces surgical time, and enhances patient outcomes.
Mechanical Part Manufacturing
This method transforms mould tooling and conformal cooling channels in manufacturing processes. Unlike traditional machining, metal 3D printing precisely with processes like MJF (Multi Jet Fusion) adds material where needed, allowing for intricate shapes and complex internal features.
This direct fabrication approach eliminates the need for costly tooling. It reduces lead times, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and low-volume production of moulds and components with integrated cooling channels.
Automobile Sector
While primarily used for prototyping, automakers are exploring its potential for higher-volume production. For example, some companies are investing in fully automated additive manufacturing lines for mass-producing automotive components.
However, beyond production, metal additive manufacturing also aids automotive restoration by providing spare parts for vintage or rare vehicles and enabling the repair of damaged components without costly tooling.

Components benefiting from this technology range from engine parts and chassis components to interior trim pieces and specialised tooling. As the automotive sector embraces innovation, metal additive manufacturing is positioned to revolutionise production and restoration processes, enhancing efficiency and sustainability.
Energy Sector
Metal additive manufacturing revolutionises the production of heat exchangers and energy-efficient components by offering unparalleled design freedom. This process allows for the fabrication of complex structures with optimised flow paths and surface areas.
As a result, these intricate internal geometries enhance heat transfer efficiency by promoting better fluid flow and increasing the contact area between fluids. This reduces energy losses and improves the overall performance of heat exchangers and energy-efficient components.
Architecture and Interior Designing
In architecture, metal additive manufacturing works by translating digital designs into physical architectural elements layer by layer. This process allows for the creation of intricate and customised features. For instance, complex facades and decorative elements can be directly 3D printed.
Also, in interior design, metal additive manufacturing enables designers to prototype and produce unique furnishings and fixtures by selectively depositing metal powder layer by layer according to digital designs. This approach provides flexibility in experimenting with shapes and materials, resulting in customised interior designs.
Consumer Goods
When it comes to jewellery and fashion accessories, this technology enables the creation of personalised pieces tailored to individual tastes. Sporting equipment benefits from optimised designs, with lightweight and durable components enhancing performance.

Home décor and gadgets become expressions of personal style, with custom-designed products adding a unique touch to living spaces.
Additionally, metal additive manufacturing facilitates small-scale production of niche consumer products, catering to specialised markets and individual preferences.
Wrapping Up
Metal additive manufacturing opens doors to lots of cool stuff in different fields. It helps make things like custom medical bits and bobs for people or super light parts for planes and spaceships. It’s like a new way to build stuff that’s more precise and lets us make things we couldn’t before.
With this tech, we’re entering a world where we can make things faster and better. As industries continue to harness their capabilities, metal additive manufacturing paves the way for unprecedented advancements, shaping a future where creativity and precision converge to redefine what’s possible in manufacturing.
Looking for 3D printing services for the production of complex and customised geometries?
Let Dainsta get you started.